What Is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work?
Okay, let’s talk DeFi. It’s not just another buzzword it’s a whole new way of looking at finance So, what is DeFi? Well, think of it as a financial system that ditches the traditional middlemen banks, brokerages, all those guys. Instead, it uses blockchain tech to let us do peer-to-peer transactions using cool things called decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. These smart contracts? They’re like agreements written in code that execute themselves. Pretty neat, right? It means automated, trust-less transactions for everyone.

The DeFi Revolution
Honestly, the rise of DeFi has been nothing short of explosive. It’s all thanks to more people embracing blockchain. The numbers are staggering. Back in 2023, the global DeFi market was worth around $21.3 billion, and get this it’s projected to hit about $616.1 billion by 2033 That’s a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 40%. What’s driving this? Well, I see a few key things:
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can jump in. No matter where you are, you can access DeFi services without needing a traditional bank.
- Cost Efficiency: Cut out the intermediaries, and suddenly, transactions become way cheaper. You get to keep more of your money.
- Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a public blockchain. Anyone can audit and verify them, building trust in the system.
How Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Works
So, how does this all actually work? DeFi is built on a mix of technologies and platforms that create open, trust-less, and non-custodial financial services. Here’s what I see as the key components
Smart Contracts
I think of smart contracts as the heart of DeFi. They make programmable financial agreements possible, automating transactions without needing anyone to oversee things. The terms are right there in the code, ensuring everyone sticks to the deal. They handle everything from lending and borrowing to yield farming and providing liquidity.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
DApps are apps that run on blockchain networks. Compared to traditional apps, they’re more secure, transparent, and autonomous. They’re powered by smart contracts and operate on a peer-to-peer network, so there’s no central authority calling the shots. DApps allow us to interact directly, managing our data and assets without relying on those traditional middlemen.
DeFi Protocols
DeFi protocols are autonomous programs designed to fix some of the issues in traditional finance. Think of platforms like Compound, Aave, and Uniswap. They offer lending, borrowing, and decentralized trading. They use smart contracts to manage transactions and financial activities, making sure we stay in control of our assets.
Blockchain Interoperability
I believe blockchain interoperability is crucial for DeFi’s future. It allows different blockchain networks to talk to each other and exchange assets easily. Protocols like Ren and Cosmos are making cross-chain transactions possible, which makes DeFi services more efficient and accessible across different platforms. It’s all about creating a more connected and open financial world.
Key Components in Action
- Liquidity Pools: These are pools of funds locked in smart contracts. They make it easier to lend, borrow, and trade on decentralized exchanges. We can earn interest or governance tokens by adding liquidity to these pools.
- Non-Custodial Wallets: These wallets let us store and manage our digital assets without needing a third party. We stay in control, which boosts security and privacy.
- Trustless Transactions: DeFi enables trustless transactions by using smart contracts. These enforce agreements without intermediaries, reducing fraud and increasing efficiency.
DeFi in Motion
- User Interaction: We access DeFi platforms through web or mobile apps, using services like lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming.
- Smart Contract Execution: Smart contracts manage transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. They automatically execute when certain conditions are met.
- Blockchain Verification: Transactions are recorded on the blockchain and verified by network participants, ensuring transparency and security.
- Cross-Chain Interactions: Interoperability protocols enable seamless interactions between different blockchain networks, enhancing accessibility and efficiency.
DeFi works by combining smart contracts, DApps, and blockchain interoperability to create an open finance ecosystem. This supports trustless transactions and non-custodial asset management, offering greater financial inclusivity and efficiency than traditional systems.
Decentralized Finance vs Centralized Finance
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Centralized Finance (CeFi) are two completely different ways to approach financial systems. Each has its own characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Let’s compare them based on trust, control, accessibility, and liquidity. Here’s what I think
Trust
Control
Accessibility
Liquidity
Key Differences Summarized
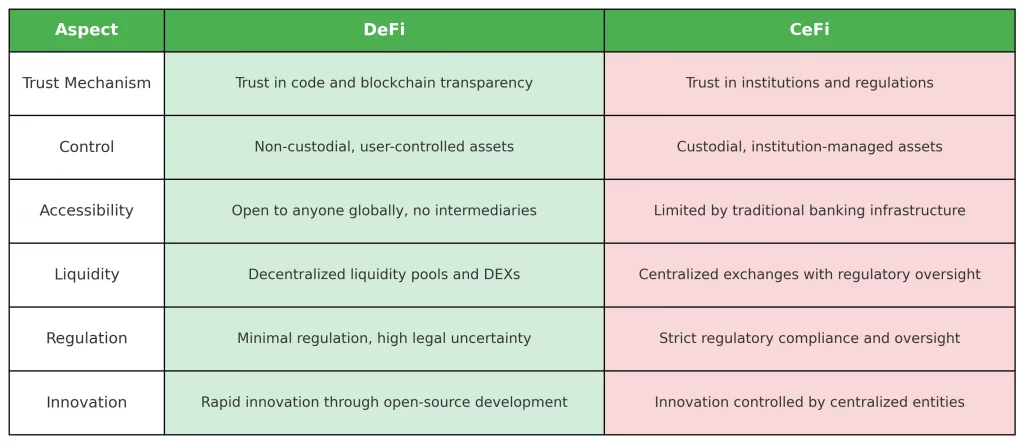
Ultimately, DeFi gives you more control and accessibility through its decentralized model. CeFi offers a more regulated and secure environment, but you have less control over your assets. Your choice depends on your risk tolerance, comfort with regulations, and desire for financial inclusivity.
Use Cases and Applications
DeFi has a wide range of uses across different financial services. It’s leveraging blockchain technology to create platforms that are decentralized, transparent, and easy to access. Here are some of the main ways I see DeFi being used
Key DeFi Use Cases
Decentralized Lending and Borrowing
These platforms allow you to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without needing intermediaries. Smart contracts automate everything, ensuring security and transparency. Borrowers put up collateral, while lenders earn interest.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs let you trade cryptocurrencies directly on the blockchain. No centralized intermediaries needed! You stay in control of your assets, and smart contracts handle the transactions.
Staking and Yield Farming
Staking involves locking up cryptocurrencies to support a blockchain network and earn rewards. Yield farming takes it a step further by providing liquidity to DeFi protocols to maximize your returns.
Asset Tokenization
This is where real-world assets are converted into digital tokens that can be traded on blockchain platforms. It makes assets like real estate and art more liquid and accessible.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are community-led organizations that are governed by smart contracts. They enable decentralized decision-making, allowing stakeholders to vote on protocol upgrades and fund allocations.
Synthetic Assets and Derivatives
These platforms let you trade synthetic assets that mimic the value of real-world assets like stocks and commodities. It gives you exposure to traditional markets without needing traditional intermediaries.
Prediction Markets
You can speculate on the outcomes of future events using blockchain-based prediction markets. These platforms automate payouts and maintain transparency using smart contracts.
Applications
Financial Services
DeFi offers lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management, all powered by blockchain tech.
Crypto Staking
You can stake cryptocurrencies to support blockchain networks and earn rewards, contributing to network security.
Decentralized Loans
DeFi lending platforms provide loans without traditional credit checks, offering quick access to funds.
Risks of Using DeFi
DeFi offers some cool financial services, but there are also significant security and financial risks. Here are some of the main things I’m concerned about
Security Risks
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts can have coding errors that hackers can exploit. These vulnerabilities can lead to major financial losses.
Protocol Exploits
DeFi protocols often interact, creating dependencies that can be exploited. For example, flash loan attacks can manipulate markets.
Centralized Points of Failure
Even though DeFi is decentralized, some components like oracles and admin keys can be centralized and vulnerable.
Financial Risks
Rug Pulls
These are scams where developers abandon a project and steal investor funds. They create a token, promote it, and then drain the liquidity pool.
Impermanent Loss
This happens when liquidity providers lose money due to changes in asset prices in a liquidity pool. Fees might not offset these losses.
Flash Loan Attacks
These involve borrowing large sums of crypto without collateral to manipulate market prices and exploit protocols.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Lack of Oversight
DeFi operates outside traditional regulatory frameworks, which creates uncertainty and risk. Regulatory actions can affect DeFi platforms and assets.
Financial Scams
The unregulated nature of DeFi makes it vulnerable to scams. You have to be careful to avoid these schemes.
🛡️ How I'm Trying to Stay Safe 🛡️
Do Your Homework: Research project reputation, audits, and community feedback.
Stick to Reputable Platforms: Use well-audited DeFi protocols.
Stay Informed: Keep up with regulatory and market updates.
Diversify: Spread investments to minimize risk.
Regulatory Challenges and the Future of DeFi
Regulatory Frameworks
European Union’s MiCA, DORA, and NIS2: The EU is leading the way with these frameworks, which aim to protect investors but challenge DeFi’s decentralized ethos.
AML/KYC Compliance Challenges: DeFi’s pseudonymous nature clashes with traditional anti-money laundering rules. Solutions like zero-knowledge proofs are being explored, but adoption is slow.
Impact on Traditional Banking
DeFi platforms offer higher yields and lower fees than traditional banks, pushing institutions to adopt hybrid models. Banks are integrating blockchain for faster settlements, and institutional DeFi participation is growing.
Global Regulatory Divergence
The EU is proactive with regulation, while the US might ease enforcement. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) emphasizes AML compliance, but it's hard to enforce in decentralized ecosystems.
Future Risks and Opportunities
Key Challenges: Security vulnerabilities, scalability issues, and compliance costs remain significant challenges.
Emerging Trends: Cross-chain integration, AI-enhanced protocols, and regulated DeFi platforms are on the horizon.
Conclusion
DeFi’s future depends on navigating regulatory complexity without losing its core principles. Innovations in identity, cross-chain interoperability, and AI-driven security will be essential. As banks and regulators adapt, collaboration will drive DeFi's integration into the mainstream.

