Understand Crypto Like a Pro 80 Key Terms Explained
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the financial world, introducing a new language of blockchain technology, decentralized systems, and digital assets. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding key crypto terms is essential to navigate this dynamic space. From blockchain basics to DeFi and NFTs, this guide covers the most important cryptocurrency terms you should know. Let’s dive into the crypto glossary and decode the crypto lingo that defines this innovative industry.

Blockchain Basics
Blockchain
A decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. Each block contains a list of transactions and is linked to the previous block, forming a chain.
Decentralization
The distribution of authority, control, and decision-making away from a central entity. In blockchain, this means no single entity controls the entire network.
Public Ledger
A transparent record of all transactions on a blockchain, accessible to anyone. This feature enhances trust and accountability.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
A technology that enables the sharing and synchronization of data across multiple locations, ensuring that all participants have access to the same information.
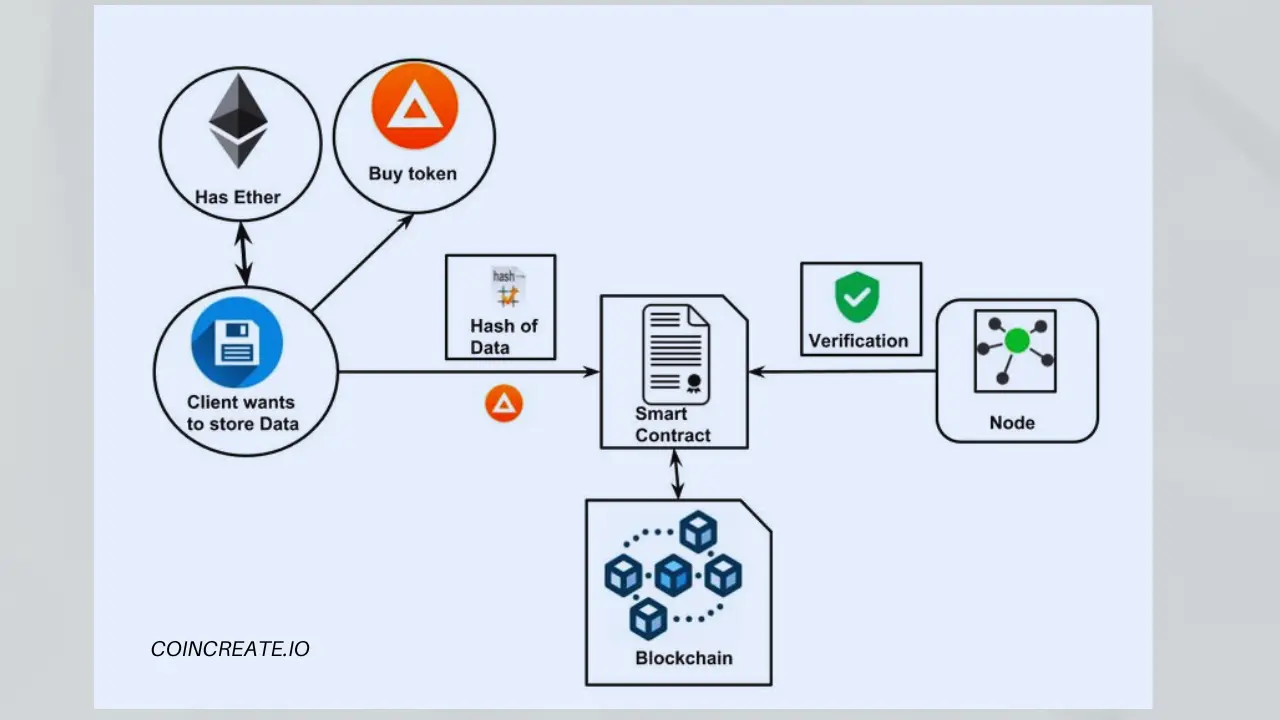
Node
A computer connected to the blockchain network that validates and relays transactions. Nodes maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanism
The method by which nodes agree on the validity of transactions. Common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Cryptography
The practice of securing information through mathematical techniques, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Cryptographic Hash
A function that converts input data into a fixed-size string of characters, which appears random. It is used for securing data in blocks.
Hash Function
An algorithm that transforms input data into a hash value. It ensures that even a small change in input results in a drastically different hash.
Merkle Tree
A data structure used in blockchain to efficiently verify and organize large amounts of data. Each leaf node is a hash of transaction data, while non-leaf nodes are hashes of their child nodes.
Block Height
The number of blocks in the blockchain preceding a specific block. It indicates how far back the block is in the chain.
Double Spending
A risk unique to digital currencies where the same coin is spent more than once. Blockchain technology mitigates this risk through consensus mechanisms.
51% Attack
A situation where an individual or group controls over 50% of the network’s mining power, potentially allowing them to manipulate transactions or double-spend coins.
Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin (BTC)
The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It introduced the concept of decentralized currency.
Ethereum (ETH)
A blockchain platform enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). It introduced the concept of programmable money.
Altcoin
Any cryptocurrency besides Bitcoin. Examples include Ethereum (smart contracts), Tether (stablecoin), and Solana (high-speed transactions). Altcoins often innovate on Bitcoin’s framework, offering features like faster settlements or energy efficiency.
Stablecoin
A type of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value by pegging it to an asset like fiat currency or commodities.
Stablecoin Peg
The mechanism by which a stablecoin maintains its value against another asset, often through reserves or algorithms.
Fiat Currency
Government-issued currency not backed by a physical commodity but rather by trust in the government. Examples include USD and EUR.
Satoshi Nakamoto
The pseudonymous creator(s) of Bitcoin, whose identity remains unknown. The smallest unit of Bitcoin is named “satoshi” in their honor.
Wallets & Security
Wallet
A digital tool for storing cryptocurrencies. Wallets can be software-based (hot wallets) or hardware-based (cold wallets).
Private Key
A secret code that allows access to your cryptocurrency holdings. It must be kept secure; losing it means losing access to your funds.
Public Key
An address derived from your private key that others can use to send you cryptocurrency. It can be shared openly without compromising security.
Seed Phrase
A series of words generated by your wallet that can restore access to your wallet if lost. It’s crucial to keep it secure.
Cold Wallet
An offline storage method for cryptocurrencies, providing enhanced security against online threats (e.g., hardware wallets).
Cold Wallet Example – Ledger Nano X:
- Used by institutions like Fidelity Digital Assets, it combines secure element chips with CC EAL6+ certification (military-grade encryption).
- Audited by third-party firms like Kudelski Security, with zero critical vulnerabilities found since 2014
Hot Wallet
An online wallet connected to the internet, offering convenience but lower security compared to cold wallets (e.g., exchange wallets).
Custodial Wallet
A wallet where a third party holds your private keys on your behalf. This offers convenience but requires trust in the custodian.
Non-Custodial Wallet
A wallet where you control your private keys, providing greater security and autonomy over your funds.
Transactions & Fees
Gas Fee
A fee paid to miners for processing transactions on networks like Ethereum. It compensates them for computational work.
Mempool
The collection of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be processed by miners. Each node maintains its own mempool.
Slippage
The difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price due to market fluctuations or low liquidity during execution.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
Trading directly between parties rather than through an exchange, often used for large transactions to avoid market impact.
Atomic Swap
A technology enabling peer-to-peer exchanges between different cryptocurrencies without intermediaries or centralized exchanges.
Mining & Validation
Mining
The process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain through solving complex mathematical problems (used primarily in PoW systems).
Proof of Work (PoW)
A consensus mechanism requiring miners to solve cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks (e.g., Bitcoin).
Proof of Stake (PoS)
A consensus mechanism where validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Staking
The process of participating in PoS networks by locking up coins in a wallet to support network operations like transaction validation while earning rewards.
Block Reward
The incentive given to miners or validators for successfully adding a new block to the blockchain, usually consisting of newly minted coins plus transaction fees.
Halving
An event in certain cryptocurrencies where block rewards are cut in half, reducing the rate at which new coins are created (notably occurring in Bitcoin).
Smart Contracts & DApps
Smart Contract
Self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code on the blockchain. They automatically enforce agreements without intermediaries.
DApp (Decentralized Application)
Applications built on blockchain technology that operate without central authority, often utilizing smart contracts for functionality.
Oracle
An external data source that provides real-world information to smart contracts on the blockchain, enabling them to interact with off-chain data.
Mainnet
The primary network where live transactions occur on a blockchain platform after testing phases are complete on testnets.
Testnet
An experimental version of a blockchain used for testing applications without risking real assets or affecting live networks.
Tokens & Tokenomics
Token
A digital asset created on an existing blockchain representing various utilities or assets within its ecosystem (e.g., ERC-20 tokens on Ethereum).
Tokenomics
The study and design of token economics within an ecosystem, including supply dynamics, distribution methods, and incentives for holders and users.
Governance Token
Tokens that grant holders voting rights within a decentralized organization or protocol, allowing them to influence decisions regarding project development or changes.
ICO (Initial Coin Offering)
A fundraising method where new cryptocurrencies sell tokens in exchange for established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum before launching their project.
Airdrop
The distribution of free tokens or coins directly into users’ wallets as part of marketing strategies or community engagement efforts by projects.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
Financial services provided through decentralized platforms without traditional intermediaries like banks, enabling lending, trading, and earning interest on crypto assets.
Yield Farming
The practice of earning rewards by providing liquidity or lending assets within DeFi protocols; users often switch between platforms for optimal returns.
Liquidity Pool
Collections of funds locked in smart contracts used for facilitating trading pairs on decentralized exchanges while providing liquidity incentives for users who contribute funds.
Impermanent Loss
The potential loss incurred when providing liquidity to automated market makers due to price fluctuations between paired assets compared with holding them separately.
Flash Loan
Uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within one transaction block; they allow users quick access to capital for arbitrage opportunities without upfront collateral requirements.
Collateral
Assets pledged as security against loans within DeFi protocols; if borrowers default on their obligations, collateral may be liquidated to cover losses incurred by lenders.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
NFT
Unique digital assets representing ownership over specific items such as art pieces or collectibles; they cannot be exchanged one-for-one due to their distinct characteristics.
Scaling & Interoperability
Layer 1 (Blockchain)
Base layer blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum where all transactions occur natively without reliance on additional layers for scaling solutions.
Layer 2 (Scaling Solution)
Protocols built atop existing blockchains aimed at improving scalability while maintaining security; examples include Lightning Network for Bitcoin.
Sharding
A method dividing databases into smaller pieces called shards; applied in blockchains allows parallel processing enhancing throughput.
Sidechain
A separate blockchain linked with another allowing transferability between them while maintaining distinct rulesets.
Cross-Chain
Technologies enabling interaction among different blockchains facilitating asset transfers across multiple networks.
Interoperability
The ability for different blockchain networks and protocols to communicate seamlessly with one another enhancing overall ecosystem functionality.
Advanced Concepts
Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP)
Cryptographic methods allowing one party to prove knowledge about certain information without revealing it; enhances privacy while verifying authenticity.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
Organizations governed by smart contracts enabling collective decision-making among members through voting mechanisms using governance tokens.
Whitepaper
A document outlining project goals technical specifications market analysis; serves as an informational resource during fundraising events like ICOs.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Direct exchanges between users without intermediaries facilitating trades lending services across decentralized platforms.
Trading & Market Terms
Liquidity
The ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price; higher liquidity typically indicates healthier markets.
HODL
A misspelled term meaning “hold” referring specifically towards long-term investment strategies despite market volatility.
Whale
Individuals or entities holding large amounts of cryptocurrency capable influencing market movements due their significant holdings.
Market Cap
The total value calculated by multiplying current price per unit by circulating supply; provides insight into asset size relative other cryptocurrencies.
Crypto Exchange
Platforms facilitating buying selling trading various cryptocurrencies often charge fees based upon transaction volume executed.
Crypto Derivatives
Financial instruments deriving value from underlying crypto assets allowing traders speculate price movements hedging risks associated with volatility.
Risks & Scams
Rug Pull
A malicious maneuver where developers abandon project leaving investors with worthless tokens; highlights importance conducting thorough research prior investing.
Regulations & Compliance
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Regulatory process requiring businesses verify identities customers before engaging financial transactions helping prevent fraud money laundering activities.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
Laws regulations aimed at preventing illicit activities such as money laundering through strict monitoring reporting suspicious transactions within financial systems.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering regulations governing cryptocurrency operations ensuring transparency legality protecting consumers against fraud risks associated emerging technologies.
Conclusion
Understanding these crypto terms is crucial for anyone entering the cryptocurrency space. Whether you’re exploring blockchain basics, diving into DeFi, or trading NFTs, this crypto glossary provides the foundation you need. Stay informed, stay secure, and embrace the future of finance with confidence.